
Renewing Historic Facades
As the first phase of a $4 billion dollar, 180-acre, 60 building government preservation project in Washington DC, this case study reviews the

As the first phase of a $4 billion dollar, 180-acre, 60 building government preservation project in Washington DC, this case study reviews the

Large master planned developments such as Battery Park City in Manhattan, Mission Bay in San Francisco, and Playa Vista in Los Angeles were built



It is commonly thought that fenestration U-factor is not a key determinant in the performance of facades in hot climates, and generally the focus of

This paper tells the story of a Double Skin Facade (DSF), where high performance and multi-disciplinary collaboration saves a library concept of


During the particularly cold first months of 1977 President Jimmy Carter, in what some call “The Sweater Speech,” famously noted how much energy




In 1871, a fourth level Architecture course was offered in New York City that instructed on topics such as heating, ventilation and circulation of


Energy codes across the country are progressively getting stricter and increasing the threshold for a baseline building’s energy performance.

Closed cavity facades (CCF), a configuration of Double Skin Facade (DSF), consists of a double-glazed unit on the inner layer and single glazing on


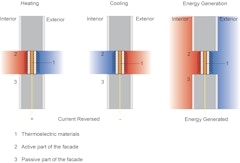
This article presents results of a research study that focuses on understanding energy performance of novel facade systems that integrate
