
ETFE Membrane Envelope Strategies
Airflow within the cavity of double-skin facades is a key component of adaptive building envelopes which change thermophysical properties to meet cha…

Airflow within the cavity of double-skin facades is a key component of adaptive building envelopes which change thermophysical properties to meet cha…

In 2015, Australia’s largest embassy complex in the world was built in Jakarta, Indonesia, to provide an official residence for Australia’s permanent…

Designing a multi-functional building envelope as an architectural façade, environmental interface and solar collector is a multi-objective explorati…

This paper outlines the successful implementation of digital workflows between the design team composed of Architect, Structural Engineer and Project…

Heat transfer through building facades can occur by any combinations of conduction, convection, and/or radiation. Conductive heat transfer depends on…

Iridescence effects, quench marks, leopard marks… The names given to optical anisotropy in toughened and heat-strengthened glass are diverse and wide…
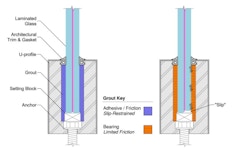
Effective thickness is a simplified method for the structural evaluation of laminated glass section properties. The method consists of defining the e…

To ensure the safety of U.S diplomatic personnel overseas, the U.S Department of State (DoS) has developed facade retrofits capable of resisting high…
Cost-effective, sustainable, self-actuating, thermally-responsive, bio-composite exo-skins that act like shields or cloaks for existing buildings cou…

A building’s envelope mitigates the effects of meteorological phenomena – including lightning – upon the structure and its occupants and contents. Th…

The research is structured around complex optical effects of undulated glass and coatings that exhibit high reflectivity, especially at higher incide…

Exterior shading devices, when typically used, are horizontal planes that are most effective at the south face of buildings in the northern hemispher…
Wind induced pressure is a major design consideration for building facades. However, the effects of facade geometry and urban terrain on wind loading…

This paper will address the potential of ornamental architectural terracotta surfaces to mitigate the effects of climate fluctuations that will creat…

Building envelopes cover a considerable part of the urban exterior surfaces, and to therefore have a significant leverage effect on the climate resil…

Analyzing the energy performance of complex building envelopes, determining the need for sun protection, and assessing the effectiveness of shading d…

There were good why reasons early US Modernism first evolved in California– wide open sites with no constraints (physical or zoning), and effectively…
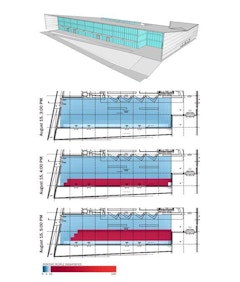
Direct sun on the body is a known potential cause of thermal discomfort for occupants, yet most thermal comfort simulations do not capture its effect…

Electrochromic (EC) glass is a seemingly magical solution to a building’s sun shading problems. A technology that was originally developed about sixt…

Manufactured veneer panels such as glass fiber reinforced concrete (GFRC), ultra high performance concrete (UHPC), sintered stone, and terracotta are…